Having covered the Build phase in our last blog on system replication within the data center, we will now cover in this blog the phase on running the data center. The run phase focuses on helping IT managers to operate and execute the data center readiness stages of disaster recovery, monitoring and administration, as well as security and auditing. In this blog, we will focus specifically on the storage and system replication technologies currently available for the IT manager.
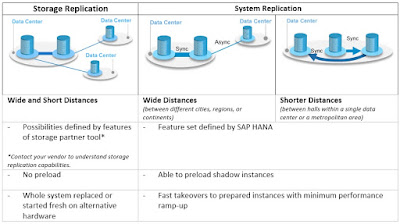
For large enterprises running multiple data centers, SAP HANA has two disaster recovery features: storage replication and system replication. These are based on the current offerings SAP HANA already has at the node level, which we covered in the previous blog. The table below provides a brief overview between the two offerings and their implications.
Table 1: Disaster recovery options between data centers, with distance in perspective
Storage & System Replication
For large enterprises running multiple data centers, SAP HANA has two disaster recovery features: storage replication and system replication. These are based on the current offerings SAP HANA already has at the node level, which we covered in the previous blog. The table below provides a brief overview between the two offerings and their implications.
Table 1: Disaster recovery options between data centers, with distance in perspective
Storage Replication
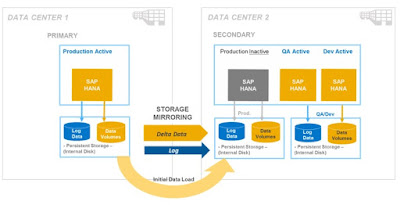
To start off, there are currently different storage replication solutions provided by several SAP partners, which mirrors data between data centers. Customers can proactively engage their dedicated hardware partners responsible for these storage replication solutions, to find out more about the existing options available that can be leveraged in their data centers. Storage data is mirrored between the persistent storage of the first and second data centers. The replicated data includes both data and log volumes.
The below example provides a closeup of how the configuration works in a data center setting. In data center 2, the production instance of SAP HANA is inactive. The mirroring in this case would occur one level below. This type of configuration would help increase the efficient use of hardware assets, by using the hardware infrastructure to also support quality assurance and development activities. To ensure that there is no impact on the mirroring process, the nonproduction usage in this case would use an area of persistent storage that is separate from the actively used production disk.
Figure 1. Storage Replication between Data Centers
System Replication – Optimized for Cost
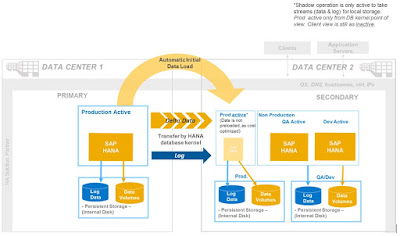
Aside from the storage replication option above, system replication is another option that can be leveraged and configured for disaster recovery scenarios. It can also be further optimized for cost or performance, depending on the needs of the business department. In the below closeup example, this configuration could be setup to help lower the TCO by maximizing the usage of hardware assets in the secondary data center for quality assurance and development.
In this configuration, production is active on the secondary cluster, but only at a minimal to take both data and log streams into local storage. Data is not preloaded. As such, the active non-production instances used by Development and Quality-Assurance will have “more room” to run in memory. The disk arrays of the instances in this setup would be separated from each other, so as not to impact performance.
Figure 2. System Replication optimized for costs
System Replication – Optimized for Performance
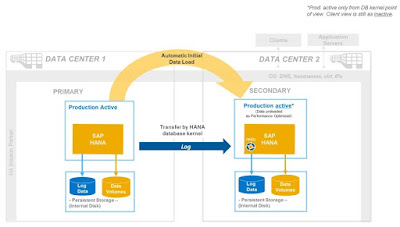
For the Performance optimized setup, the IT assets are used solely only for a takeover to ensure as minimum impact to the performance as possible. This can be a preferred option for enterprises with mission critical workloads and extremely short recovery time objectives. Data is also preloaded in this case.
In this configuration, the secondary instance will manage the replication process. As the instance appears active only from a database-kernel point of view, from the client view the secondary server cannot be actively accessed. The introduction of the continuous log replay feature in SAP HANA SPS11 takes the system replication feature a step further by removing the need to transfer the delta data. Only the log information is transferred via the SAP HANA database kernel, and this feature helps to minimize traffic on the connecting network, while further reducing takeover times.
Figure 3. System Replication optimized for Performance
System Replication – Summary
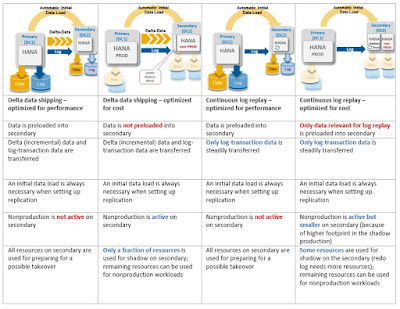
To put it all together, the table below provides a summary of the differences between the available disaster recovery options, which are based on the system replication methods focusing on the node level, as highlighted in the previous blog.
Table 2. Comparison between different system replication options
Monitoring and Administration in the Data Centers
Aside from choosing the replication methods, there are also various options and tools available for IT managers to specifically manage their SAP HANA landscape within the data center. Below are some of the tools that an IT manager can consider to manage their SAP HANA data center landscape:
- SAP HANA cockpit: To monitor and administer the SAP HANA, the SAP HANA cockpit is a platform-independent tool to help administer, monitor and manage the SAP HANA implementation. With this application, IT managers can monitor databases, navigate between different actions and handle central configuration tasks.
- SAP Solution Manager: The SAP Solution Manager offers a holistic monitoring option for SAP HANA and its environments. This tool is also used by SAP support personnel to assist in early problem analysis.
- SAP Landscape Management: The SAP Landscape Management software allows IT managers to orchestrate SAP HANA. It interacts with SAP Solution Manager and also incorporates SAP HANA cockpit tiles. This integration supports enhanced orchestration and automated functions. SAP Landscape Management offers features from basic operation to larger and more complex SAP solution landscapes, such as database and application system copies or automated zero downtime updates on shadow systems with SAP HANA replication features.
No comments:
Post a Comment