Common machine learning scenarios such as fraud detection, customer churn, employee flight risk, aim to predict Yes/No outcomes using binary classification models. But sometimes the target to predict has more than just two classes. This is the case of Delivery Timeliness that can have three categories: Early/On-time/Late.
From this article you will learn how to train and apply a multiclass classification model in a Python notebook with HANA ML APL.
The following example was built using HANA ML 2.12.220325 and APL 2209.
Census Income will be our training dataset.
from hana_ml import dataframe as hd
conn = hd.ConnectionContext(userkey='MLMDA_KEY')
sql_cmd = """
select * from apl_samples.census
where "marital-status" not in (
select "marital-status" from apl_samples.census
group by "marital-status" having count(*) < 1500 )
order by "id"
"""
hfd_train = hd.DataFrame(conn, sql_cmd)
hfd_train.head(5).collect().style.hide_index()
Let’s check the size of the HANA dataframe in number of rows.
hfd_train.shape[0]
Marital status is our multiclass target.
col_key = 'id'
col_target = 'marital-status'
col_predictors = hfd_train.columns
col_predictors.remove(col_key)
col_predictors.remove(col_target)
col_predictors.remove('education-num')
len(col_predictors)
We do a fit and ask for a final model with no more than six variables. The processing is done within the HANA database.
from hana_ml.algorithms.apl.gradient_boosting_classification import GradientBoostingClassifier
apl_model = GradientBoostingClassifier()
apl_model.set_params(variable_selection_max_nb_of_final_variables = '6',
other_train_apl_aliases={'APL/VariableAutoSelection':'true'})
apl_model.fit(hfd_train, label=col_target, key=col_key, features=col_predictors)
The target distribution looks like this:
my_filter = "\"Partition\" = 'Estimation'"
df = apl_model.get_debrief_report('MultiClassTarget_Statistics').filter(my_filter).collect()
df.drop('Oid', axis=1, inplace=True)
df.drop('Target Key', axis=1, inplace=True)
format_dict = {'% Weight':'{:,.2f}%', 'Weight':'{:,.0f}'}
df.style.format(format_dict).hide_index()

At this point we choose to save the APL trained model.
from hana_ml.model_storage import ModelStorage
model_storage = ModelStorage(connection_context=conn, schema='USER_APL')
apl_model.name = 'My Multiclass Model'
model_storage.save_model(model=apl_model, if_exists='replace')
model_storage.list_models()
One hour or one day later …
We are back. We load our multiclass model.
from hana_ml import dataframe as hd
conn = hd.ConnectionContext(userkey='MLMDA_KEY')
from hana_ml.model_storage import ModelStorage
model_storage = ModelStorage(connection_context=conn, schema='USER_APL')
apl_model = model_storage.load_model(name='My Multiclass Model')
apl_model.get_model_info()
We request the model reports and display first the accuracy overall.
from hana_ml.visualizers.unified_report import UnifiedReport
UnifiedReport(apl_model).build().display()
We take a deeper look with the class-by-class report:
Here are the variables that APL selected.
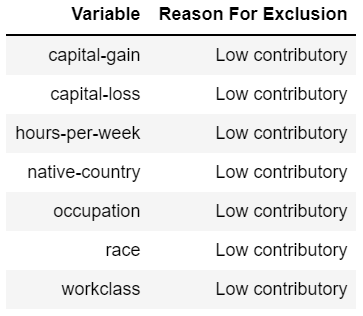
We want to know which variables were excluded during the training, and why:
df = apl_model.get_debrief_report('ClassificationRegression_VariablesExclusion').collect()
df = df[['Variable', 'Reason For Exclusion']]
df.style.hide_index()
We define a new dataframe with a few rows to try the APL model.
sql_cmd = 'select * from apl_samples.census where "id" between 550 and 554 order by "id"'
hfd_apply = hd.DataFrame(conn, sql_cmd)
hfd_apply.collect().style.hide_index()
We do a predict and ask for the top three reasons. Again, the processing is done within the database.
apl_model.set_params( extra_applyout_settings=
{ 'APL/ApplyExtraMode': 'Advanced Apply Settings',
'APL/ApplyPredictedValue': 'false',
'APL/ApplyProbability': 'false',
'APL/ApplyDecision': 'true',
'APL/ApplyReasonCode/TopCount': '3',
'APL/ApplyReasonCode/ShowStrengthValue': 'false',
'APL/ApplyReasonCode/ShowStrengthIndicator': 'false' }
)
df = apl_model.predict(hfd_apply).collect()
df.columns = ['Id', 'Actual', 'Prediction', 'Reason 1 Name', 'Reason 1 Value', 'Reason 2 Name', 'Reason 2 Value', 'Reason 3 Name', 'Reason 3 Value']
df.style.format({'Probability': '{:,.2%}'.format}).hide_index()

One can also request the score for each class. The class with the highest score becomes the prediction.
apl_model.set_params( extra_applyout_settings=
{ 'APL/ApplyExtraMode': 'Advanced Apply Settings',
'APL/ApplyPredictedValue': 'true',
'APL/ApplyProbability': 'false',
'APL/ApplyDecision': 'true',
}
)
df = apl_model.predict(hfd_apply).collect()
df.rename(columns={'TRUE_LABEL': 'Actual','PREDICTED': 'Prediction'}, inplace=True)
df.columns = [hdr.replace("gb_score_marital-status_", "") for hdr in df]
df.style.hide_index()
Another option is to export the model equation for scoring in stand-alone JavaScript.
apl_scoring_equation = apl_model.export_apply_code(code_type='JSON')
text_file = open("apl_model.json", "w")
text_file.write(apl_scoring_equation)
text_file.close()
Source: sap.com









No comments:
Post a Comment